Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are essential components in modern electronic devices like smartphones, tablets, and computers. These intricate boards are vulnerable to a wide range of contaminants, which can affect their performance. Cleaning a PCB properly is critical to ensure its functionality, especially when contamination occurs without visible physical damage. In this guide, we'll explore the best practices for cleaning PCBs, the types of contaminants you may encounter, and the tools and methods to effectively restore your boards to optimal condition.
Challenges in PCB Cleaning
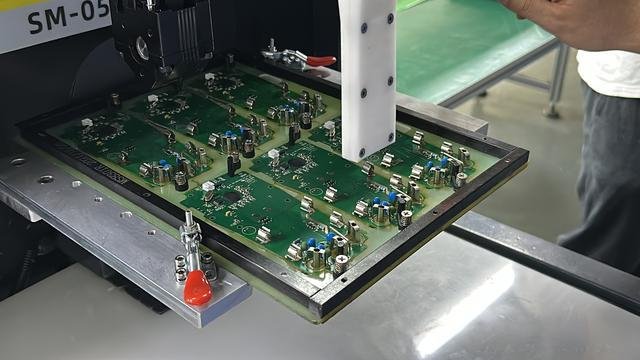
Cleaning a PCB is a delicate task that requires precision and the right approach to avoid damaging sensitive components. Printed circuit boards are made up of a variety of exposed components, such as capacitors, resistors, and integrated circuits, all of which can be easily damaged if the wrong cleaning methods are applied. The specific cleaning process largely depends on the type of contaminants you need to address.
Common contaminants on PCBs include:
- Dust and Dirt
- Wet Contaminants (Oil, Grease, and Solder Flux)
- Corrosion and Chemical Residue
- Other Environmental Pollutants
Each type of contaminant requires a specialized approach to ensure effective cleaning while preventing damage to the board.
Removing Dry Contaminants: Dust and Dirt

Dust and dirt are among the most common contaminants that accumulate on PCBs. They can interfere with the electrical components, leading to performance issues or complete failure of the device. These dry pollutants can often be managed using several gentle cleaning techniques:
1. Brushing
One of the most straightforward methods for removing dust and dirt from a PCB is using a soft-bristled brush. A fine brush, such as a paintbrush or a dedicated PCB cleaning brush, allows you to gently sweep away contaminants from the surface of the board. Make sure to use light strokes to avoid damaging fragile components.
2. Compressed Air
Compressed air is a popular method for blowing away loose dust and debris from the surface of the PCB. It is particularly useful for hard-to-reach areas such as between closely spaced components. However, excessive use of compressed air can cause static buildup or blow contaminants deeper into the board, so it should be used with caution.
3. Specialized Vacuum Cleaners
Some manufacturers use specialized vacuum cleaners designed for cleaning electronic components. These vacuums have softer suction power compared to regular household vacuums, which can prevent damage to delicate components. It is essential to avoid using standard vacuum cleaners, as they could create static charges or dislodge components.
Cleaning Wet Contaminants: Oils, Flux, and Liquids
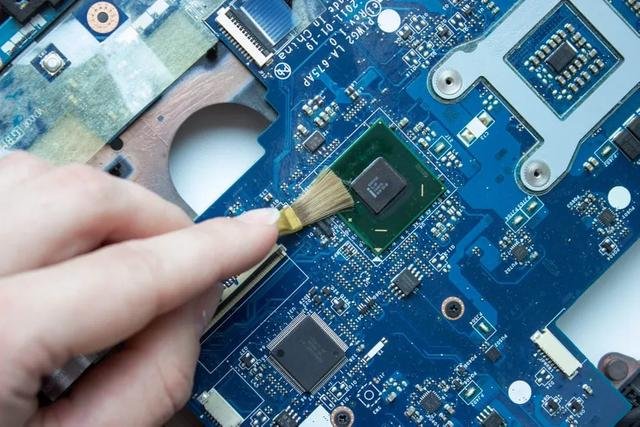

Wet contaminants, such as oil, grease, flux residues, or liquid spills, pose a unique challenge. These substances can leave behind sticky residues that attract dust and further degrade the performance of the PCB. To clean wet contaminants, the following methods are recommended:
1. Isopropyl Alcohol (IPA)
Isopropyl alcohol, particularly high-purity 99% IPA, is widely used to remove oils, flux, and other residues from PCBs. To clean the board, dip a cotton swab or soft cloth into the alcohol and gently wipe the contaminated areas. The alcohol evaporates quickly, leaving the PCB dry and free of residue. However, it is essential to perform this process in a well-ventilated area, as IPA fumes can be hazardous.
2. Deionized Water
For those who prefer to avoid alcohol or cannot access it, deionized water is a suitable alternative. It can effectively remove residues like flux or oils without causing damage to the PCB. However, when using water, it’s crucial to minimize exposure to moisture, ensuring that the PCB is thoroughly dried before reassembly. This method works best when the PCB is exposed to light contamination and not heavy residues.
3. PCB-Specific Cleaning Solutions
Several electronic cleaning solutions are designed to break down tough residues like oil or flux. These solutions are typically available from electronics retailers or wholesalers. It’s essential to choose a cleaning solution that is compatible with your PCB material and contamination type. Be cautious when selecting strong cleaning agents, as they may damage plastics or erase board markings. Test the cleaner on a non-essential or older PCB before applying it to your device.
Advanced Cleaning: Ultrasonic PCB Cleaning

For highly contaminated or intricate PCBs, ultrasonic cleaning is an effective solution. This process uses high-frequency sound waves to agitate a cleaning solution and create microscopic bubbles that implode, producing a scrubbing effect. This method is ideal for removing contaminants from hard-to-reach areas without damaging the components.
Ultrasonic cleaning works by immersing the PCB in a tank filled with a cleaning solution. The ultrasonic waves cause billions of tiny bubbles to form and collapse, dislodging contaminants from even the smallest crevices on the board. The benefits of ultrasonic cleaning include:
- Precision Cleaning: Capable of cleaning components with tight tolerances and intricate designs.
- Non-Destructive: When performed correctly, ultrasonic cleaning can be gentle on the PCB, unlike manual scrubbing.
- Efficiency: It is a fast method that can clean multiple boards simultaneously.
However, ultrasonic cleaning comes with a few precautions. Excessive power levels or prolonged exposure can damage sensitive components, including solder joints and surface-mounted devices. It’s recommended to test the ultrasonic cleaner on an old or non-critical PCB first before cleaning high-value electronics.
Maintaining PCB Cleanliness Post-Cleaning
Once your PCB is cleaned, it's crucial to ensure that it remains contaminant-free. For long-term protection, consider the following tips:
- Proper Storage: Store PCBs in a clean, dry, and static-free environment to avoid dust and moisture buildup.
- Antistatic Packaging: Use antistatic bags or containers when transporting or storing PCBs to reduce the risk of electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage.
- Regular Inspections: Periodically inspect the PCB for signs of contamination or wear. Early detection of issues can prevent more severe damage.
Conclusion
Cleaning a printed circuit board is a crucial step in maintaining the longevity and functionality of electronic devices. Whether you're dealing with dust, oil, flux, or moisture, selecting the right cleaning method for the type of contamination is vital. Techniques such as brushing, using isopropyl alcohol, and ultrasonic cleaning can effectively restore the board's condition without causing damage. However, it's essential to be cautious and avoid over-aggressive cleaning methods that could harm delicate components. With proper care and attention, your PCBs will continue to perform at their best, contributing to the reliability of your electronic devices.
For businesses or individuals working with PCBs on a regular basis, staying informed about the latest cleaning technologies and practices is crucial. Investing in the right tools and understanding the best techniques can significantly extend the life of your PCBs and reduce repair costs over time.