The Printed Circuit Board (PCB) is the backbone of any electronic device, providing the foundation on which all electronic components are mounted and interconnected. Whether it’s a smartphone, a computer, or an industrial control system, the PCB ensures that each component works together seamlessly to deliver the intended functionality.
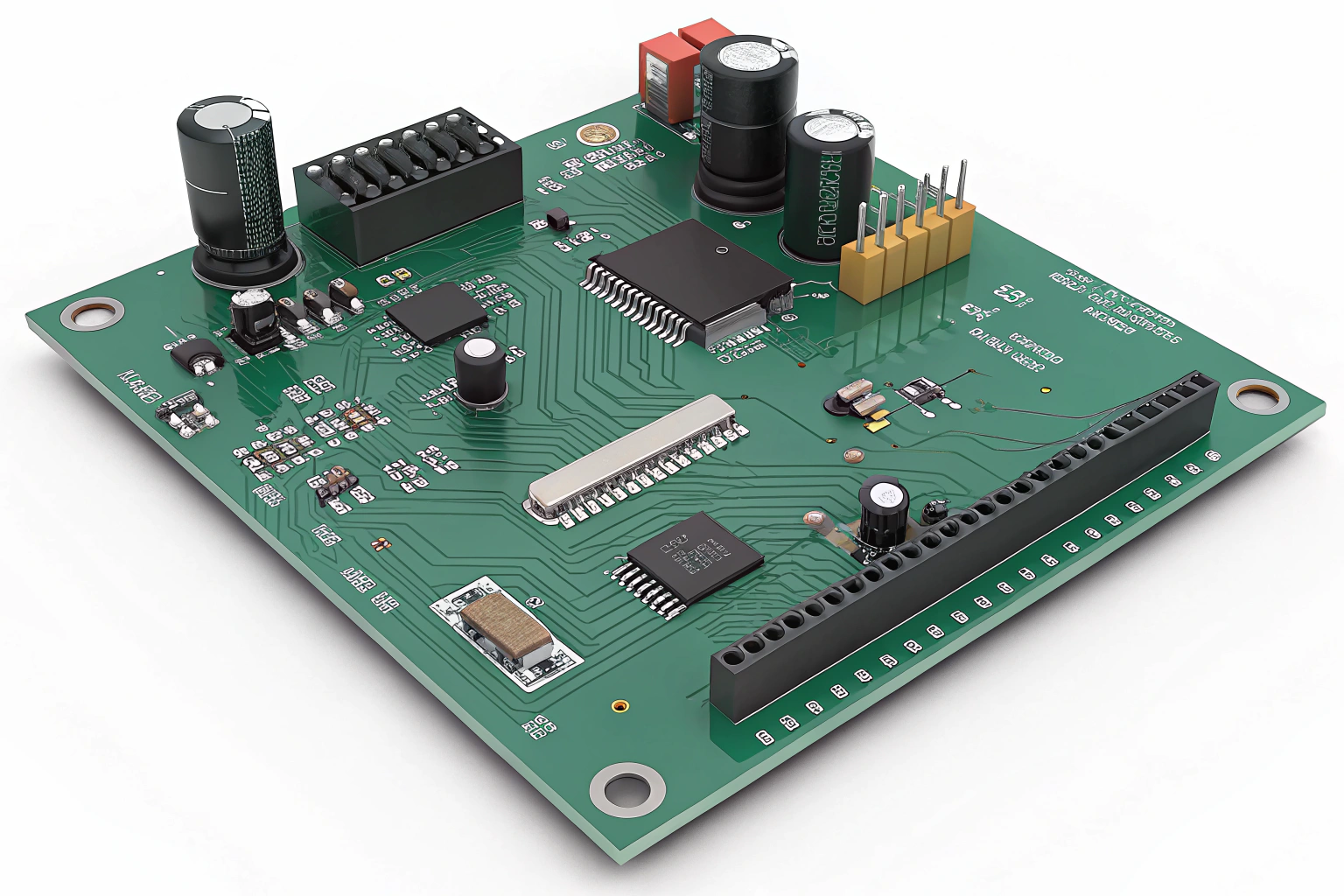
The main function of a PCB is to support and electrically connect various components such as resistors, capacitors, integrated circuits (ICs), and connectors through conductive paths or traces.
Understanding the function of a PCB board is critical for engineers and product developers as it impacts the overall design, performance, and reliability of the final product. Let’s break down the core functions and roles that the main PCB board plays in an electronic system.
Supporting Electronic Components
A PCB physically supports all the electronic components, ensuring they remain in place and properly connected.
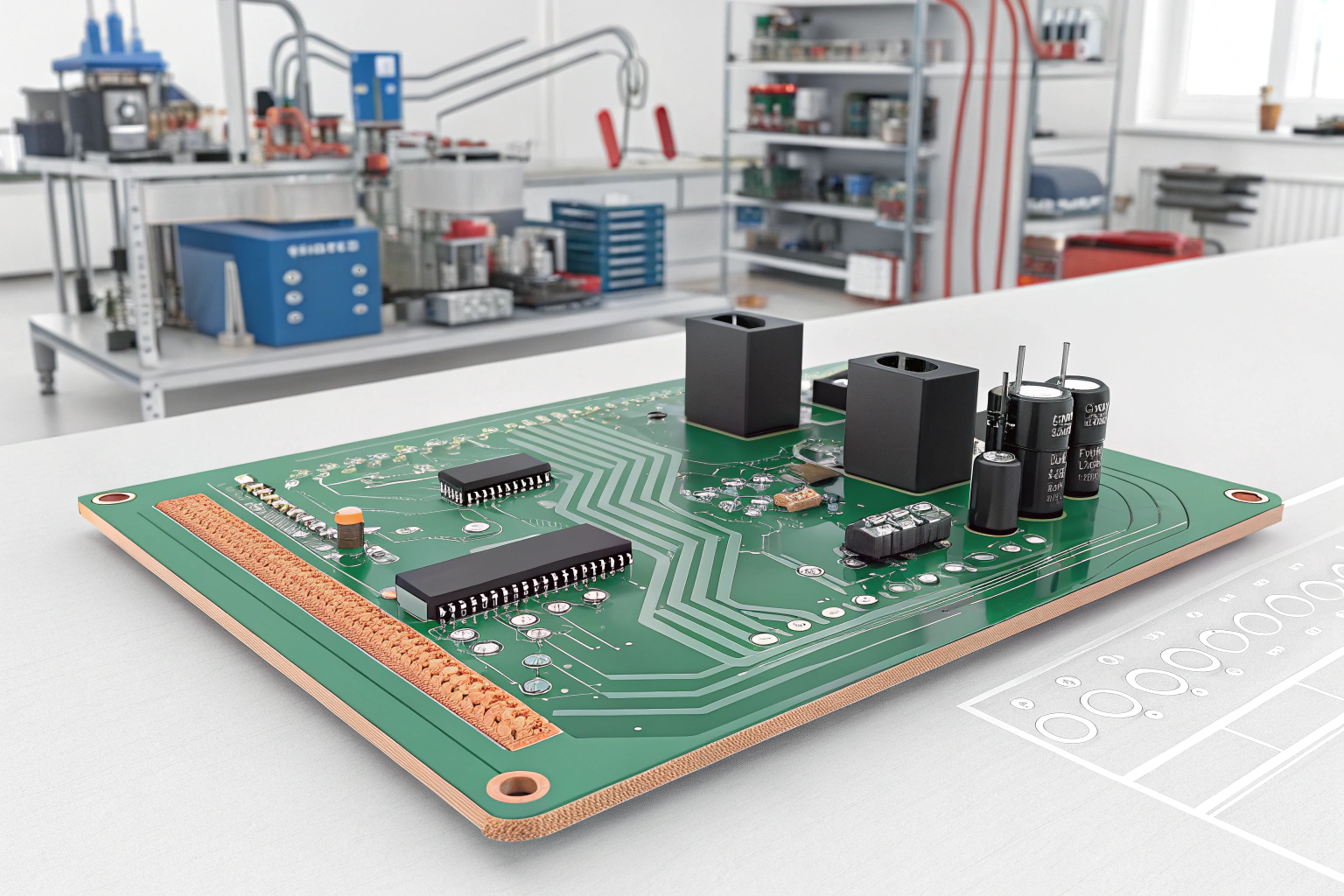
The main function of the PCB is to provide a stable platform for mounting components such as transistors, capacitors, ICs, and resistors.
Without the PCB, the electronic components would not be able to function together. The PCB connects all the components through conductive copper traces that are precisely etched to form electrical pathways. These traces allow the flow of electricity between the components, enabling the circuit to perform its specific task. In my factory, we produce PCBs with specific designs based on customer requirements to ensure that each component is securely placed for maximum performance.
Key Roles of a PCB in Supporting Components
- Mounting: Ensures components stay fixed in place
- Connectivity: Provides electrical connections between components
- Spacing: Guarantees correct spacing between components for optimal operation
This support function goes beyond just holding components in place. It ensures that each component has the appropriate spacing, correct orientation, and access to power, ground, and signal paths.
Providing Electrical Connectivity
Beyond physical support, the PCB’s primary role is to establish electrical connections between components.
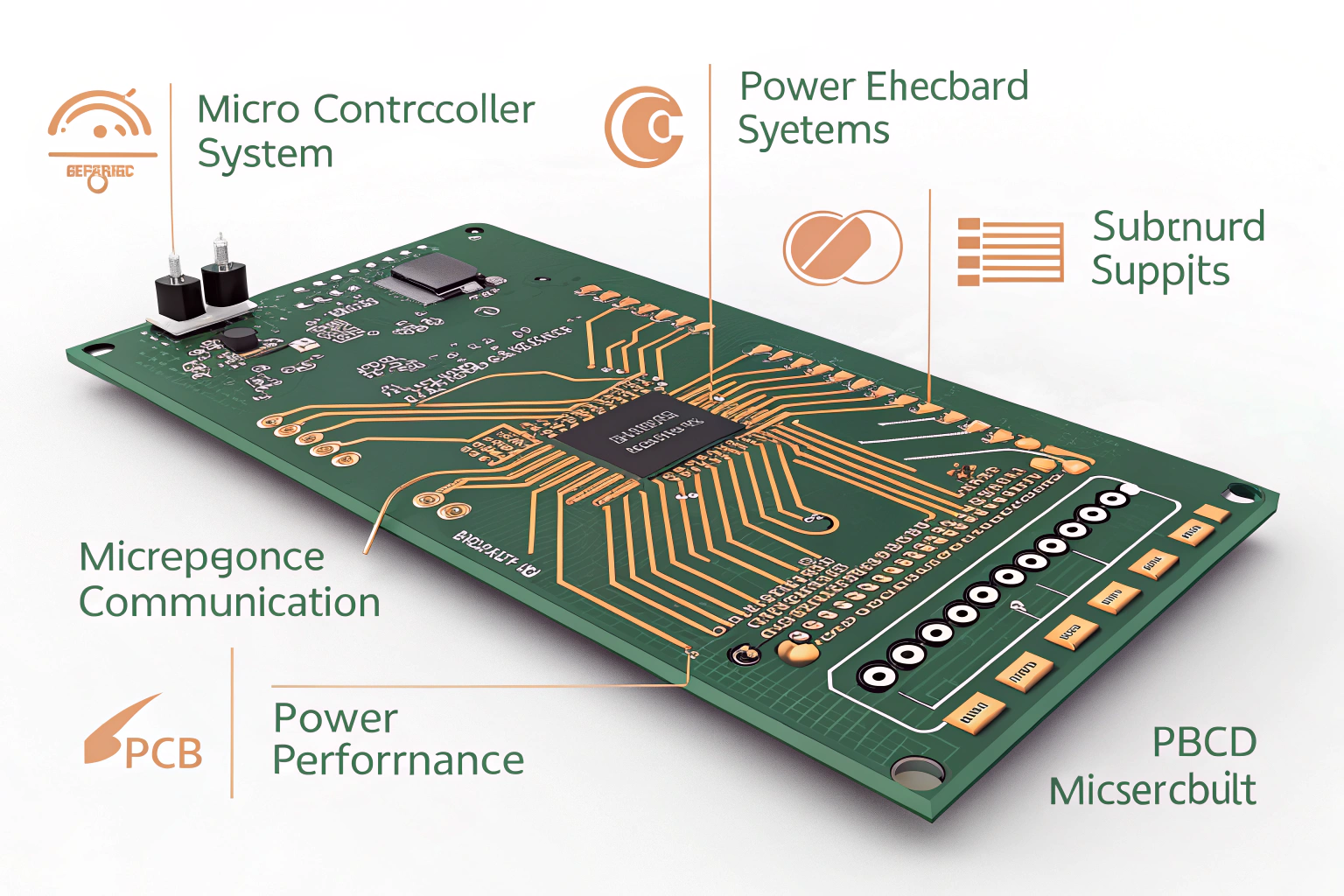
The copper traces on a PCB are designed to carry electrical signals, power, and ground between components, ensuring the circuit performs its intended functions.
For instance, in a microcontroller-based system, the PCB provides the necessary connections for the microcontroller to communicate with sensors, power supplies, and other subsystems. The well-designed PCB ensures that the signals travel efficiently and with minimal interference, which is crucial for high-performance devices like smartphones and computers.
The precise routing of electrical pathways also prevents issues like signal crosstalk or power loss. In high-frequency circuits, such as those used in wireless communication, the PCB must be engineered to minimize resistance and inductance to maintain signal integrity. We take extra care in this phase of production, especially when handling RF and high-speed digital circuits.
Managing Heat Dissipation
Electronic components, especially in power circuits, generate heat that can affect performance and reliability. The PCB helps manage this heat to maintain safe operating temperatures.
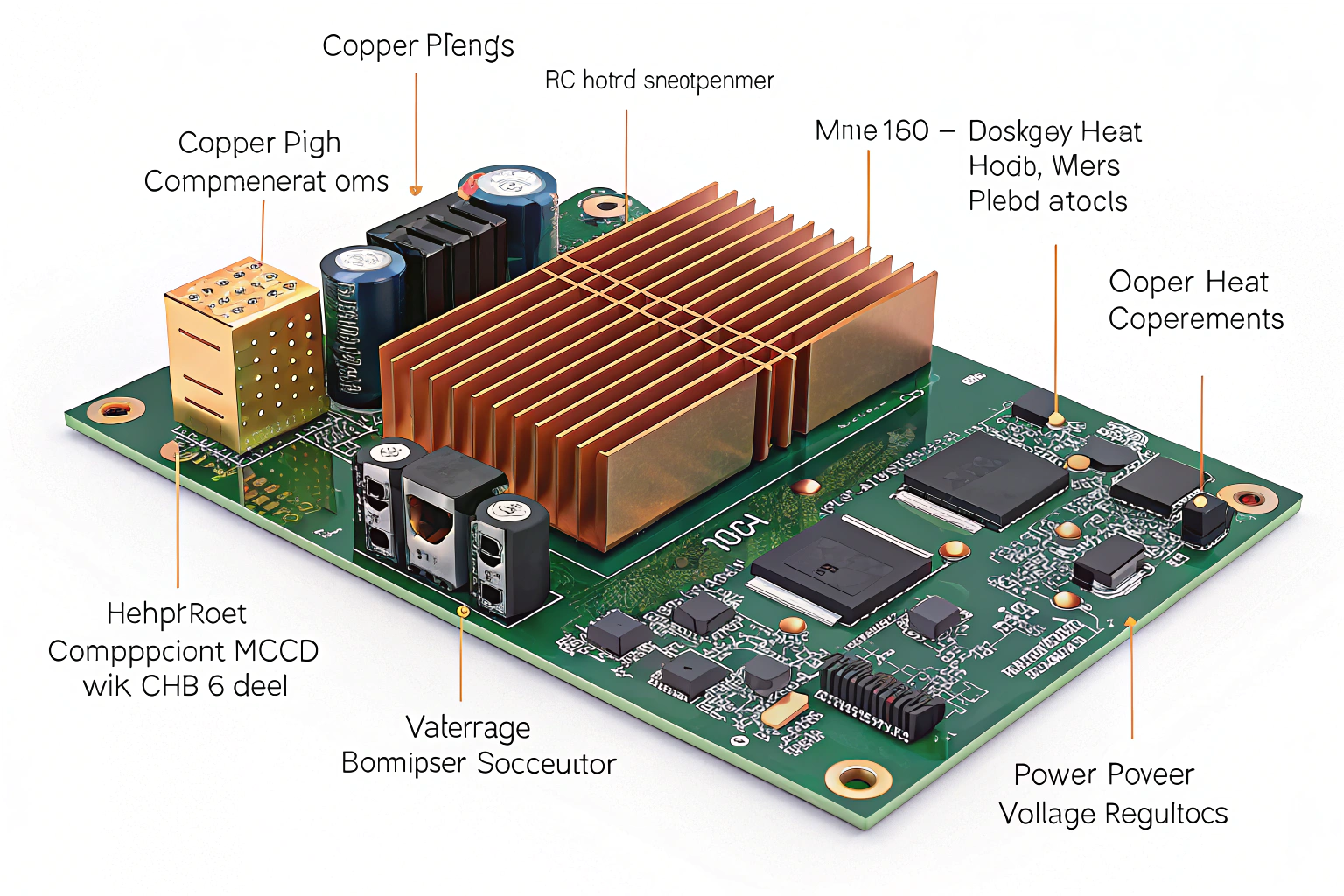
Many PCBs incorporate heat sinks, copper planes, and other design features to help dissipate heat generated by high-power components like processors or voltage regulators.
In products like LED lights or power supplies, heat management is critical to prevent thermal damage to the components. Aluminum-based PCBs are often used in such applications because of their superior thermal conductivity compared to traditional FR4 boards. In my experience, selecting the right PCB material for thermal performance is essential to ensure long-term reliability, especially in energy-intensive systems.
Enabling Signal Routing and Grounding
PCBs are also essential for providing efficient signal routing and proper grounding for components.
Signal integrity is crucial for any electronic system, and the PCB’s design determines how well signals will be transmitted without distortion or loss.
Good PCB design ensures that signals are routed in a way that minimizes noise and crosstalk between components. Proper grounding techniques, such as using ground planes, are also crucial to reduce interference and prevent grounding issues that could lead to malfunction. For instance, in digital circuits, a well-laid-out PCB will have separate ground paths for analog and digital signals to prevent unwanted interference.
Our factory uses advanced simulation tools during the PCB design phase to ensure that the routing and grounding are optimized for the specific application, particularly in high-speed or analog circuits.
Supporting Integration and Miniaturization
As technology advances, there is a growing need for smaller, more integrated electronic devices. The PCB plays a vital role in facilitating this miniaturization.
The ability to integrate multiple components into a smaller footprint is one of the key functions of a modern PCB.
Through multi-layer designs and advanced component placement techniques, a PCB allows for the integration of more functionality in a compact space. This is particularly important in consumer electronics, where size reduction is a primary concern. For instance, smartphones and wearables rely on densely packed PCBs that can accommodate processors, memory, sensors, and power management systems, all in a slim, lightweight design.
The use of advanced materials and multi-layer construction also helps achieve smaller form factors without compromising performance. In our production process, we offer both high-density interconnect (HDI) and rigid-flex PCBs to meet the needs of customers requiring advanced miniaturization.
PCB Function Comparison
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Component Support | Provides the mechanical base for components to be mounted securely. |
| Electrical Connectivity | Routes electrical signals between components using copper traces. |
| Heat Management | Dissipates heat generated by high-power components, ensuring longevity. |
| Signal Integrity | Ensures clear and accurate signal transmission with optimized routing and grounding. |
Conclusion
The main PCB board serves as the foundation for any electronic system, providing support, electrical connectivity, heat management, and signal integrity. As technology advances, PCBs are designed to be smaller, more efficient, and more reliable, playing a critical role in the performance of modern devices. Whether it’s in a smartphone, a medical device, or an industrial machine, the PCB ensures that all components work together harmoniously to deliver the desired functionality. In my factory, we take pride in producing high-quality PCBs that meet the highest standards of performance and reliability for our customers.

