In modern electronic devices, circuit boards are the core components that enable various functionalities. When you open a smartphone, computer, or any other electronic gadget, the circuit board inside is undoubtedly essential for its proper operation. While circuit boards come in various colors, blue circuit boards stand out for their unique appearance and superior performance. Not only are blue circuit boards visually striking, but their manufacturing process is also meticulously designed to ensure stability and reliability across a range of applications. In this article, we will explore the definition, advantages, manufacturing process, and applications of blue circuit boards, helping you gain a deeper understanding of this critical electronic component.
Understanding Blue Circuit Boards: The Basics

Before diving into the fascinating world of blue circuit boards, it’s essential to grasp the fundamental concepts of what circuit boards are and how they work. A circuit board, also known as a printed circuit board (PCB), is a flat circuit carrier that is created by transferring a circuit design onto an insulating substrate. Typically, these substrates are made from non-conductive materials such as fiberglass or composite epoxy resin to ensure stability and durability.
Structure and Components of Circuit Boards
The primary function of a circuit board is to provide connections and support for various electronic components. The basic structure usually includes the following parts:
- Substrate: The base layer of the circuit board is typically made from FR-4 material, which offers excellent electrical insulation and mechanical strength.
- Conductive Layer: On the surface of the substrate, conductive materials like copper form circuit “traces” that create pathways for electrical flow.
- Component Mounting: Electronic components such as resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits are securely attached to the circuit board through soldering or other methods, connecting them with the traces to form a complete circuit.
- Protective Layer: To enhance durability, the surface of the circuit board is often coated with a protective layer, such as a solder mask, to prevent oxidation and short circuits.
Working Principle
The working principle of a circuit board is relatively straightforward but critically important. Through conductive pathways, electrical current flows between different electronic components, enabling various functions. The specific process is as follows:
- Power Input: The power supply enters the circuit board through connection ports, providing necessary electricity to the circuit.
- Signal Transmission: Current travels through the traces, reaching various electronic components. These components process the current based on their designed functions, such as amplifying, filtering, or converting signals.
- Output: The processed signals are output through other connections, which may be used to drive displays, speakers, or other devices.
The Unique Aspects of Blue Circuit Boards
While circuit boards are available in a variety of colors, blue circuit boards are particularly favored for their unique appearance and functionality. The blue solder mask not only makes the circuit board visually striking but also provides better heat resistance and corrosion resistance, enhancing the overall performance of the circuit board.
In summary, circuit boards are indispensable components of modern electronic devices, and blue circuit boards stand out among them due to their distinctive design and excellent performance. In the subsequent sections, we will explore the manufacturing process, applications, and future trends of blue circuit boards in greater detail.
The Evolution of Circuit Boards: A Journey Through Time

The history of circuit boards dates back to the early 20th century, and since then, they have undergone remarkable advancements. From cumbersome manually wired circuits to the compact and efficient printed circuit boards (PCBs) we know today, the evolution of circuit boards is truly impressive. This section will explore the technological advancements that paved the way for blue circuit boards, which have become an indispensable part of modern electronic devices.
Early Beginnings
The journey of circuit boards began in the early 1900s, with the introduction of basic electrical circuits. These circuits were primarily constructed using point-to-point wiring, which was not only labor-intensive but also prone to errors and inefficiencies. The first significant step towards modern circuit boards came with the invention of the printed circuit board in the 1930s, which allowed for a more organized and reliable method of connecting electronic components.
The Advent of PCB Technology
The 1940s and 1950s saw the development of PCB technology, driven by the needs of the military and aerospace industries during World War II. PCBs offered a compact solution for integrating multiple components into a single board, significantly reducing the weight and size of electronic devices. This innovation laid the foundation for the mass production of electronic equipment, as manufacturers began to recognize the advantages of using PCBs over traditional wiring methods.
Introduction of Blue Circuit Boards
While early PCBs were primarily manufactured in green, the introduction of blue circuit boards brought about a new aesthetic and functional dimension. The blue solder mask became popular for its visually appealing look and its ability to enhance heat resistance and chemical stability. These characteristics made blue circuit boards particularly suitable for high-performance applications, such as computers and consumer electronics.
Technological Advancements
The evolution of circuit boards has been driven by several key technological advancements:
- Material Innovations: The development of advanced substrate materials, such as FR-4, significantly improved the durability and performance of circuit boards. These materials offer excellent thermal and electrical properties, making them ideal for modern applications.
- Manufacturing Techniques: Advancements in manufacturing techniques, such as automated pick-and-place machines and laser etching, have greatly increased the efficiency and precision of PCB production. These innovations allow for the mass production of complex circuit boards with intricate designs.
- Miniaturization: The demand for smaller and more powerful electronic devices has led to the miniaturization of circuit boards. Surface mount technology (SMT) enables components to be mounted directly onto the surface of the board, reducing space and weight while improving performance.
- Design Software: The emergence of sophisticated PCB design software has revolutionized the way engineers create circuit boards. These tools enable precise modeling and simulation, allowing for rapid prototyping and testing of designs before production.
The Role of Blue Circuit Boards Today
Today, blue circuit boards are widely used in various applications, from consumer electronics to medical devices and automotive systems. Their distinct appearance and superior performance characteristics make them a preferred choice for manufacturers seeking to produce reliable and efficient electronic products.
In summary, the evolution of circuit boards has been a journey marked by innovation and adaptation. Blue circuit boards stand as a testament to the advancements in technology that have transformed the electronics industry, making them essential components of modern devices. As technology continues to evolve, the future of circuit boards promises even more exciting developments on the horizon.
Advantages of Blue Circuit Boards: Beyond Aesthetics

Blue circuit boards are not only visually appealing but also come with a host of advantages that make them a popular choice in various applications. In this section, we will explore the benefits of using blue solder masks in PCBs, including enhanced aesthetics and visibility. Additionally, we will delve into how blue circuit boards are applied across different industries, making them an ideal choice for specific use cases.
Aesthetic and Visual BenefitsOne of the most apparent advantages of blue circuit boards is their striking appearance. The blue solder mask enhances the overall look of the PCB, making it stand out in a crowded market. This aesthetic appeal can be particularly beneficial for consumer electronics, where design plays a crucial role in attracting customers.Moreover, the blue color provides excellent contrast with the metallic traces and components, improving visibility during inspection and assembly. This increased visibility can lead to easier troubleshooting and maintenance, as technicians can quickly identify connections and components on the board.Enhanced Thermal PerformanceBlue circuit boards often feature high-quality materials that can withstand elevated temperatures. This characteristic is crucial in applications where heat dissipation is a concern, such as in power electronics or high-performance computing. The blue solder mask can help protect the underlying components from thermal damage, ensuring reliable operation even under demanding conditions.Chemical ResistanceThe materials used in blue circuit boards typically offer better chemical resistance compared to some other colors. This property is particularly advantageous in industries such as automotive and medical devices, where exposure to various chemicals is common. The durability of the blue solder mask helps protect the circuit board from corrosion, ensuring longevity and consistent performance.Versatility in ApplicationsBlue circuit boards find applications across a wide range of industries, including:
Consumer Electronics: The aesthetic appeal and reliability of blue circuit boards make them a popular choice in smartphones, laptops, and gaming consoles. Their enhanced visibility also aids in the manufacturing and repair processes.Automotive Industry: In automotive applications, blue circuit boards are often used in control systems and infotainment devices. Their thermal and chemical resistance is vital for ensuring safety and reliability in harsh environments.Medical Devices: The medical field requires precise and reliable electronic components. Blue circuit boards are used in diagnostic equipment, monitoring devices, and other medical technologies, where performance and safety are paramount.Industrial Automation: In automation and control systems, blue circuit boards play a critical role in ensuring the efficiency and reliability of operations. Their robustness and visibility contribute to smoother production processes and easier maintenance.
The Manufacturing Process of Blue Circuit Boards
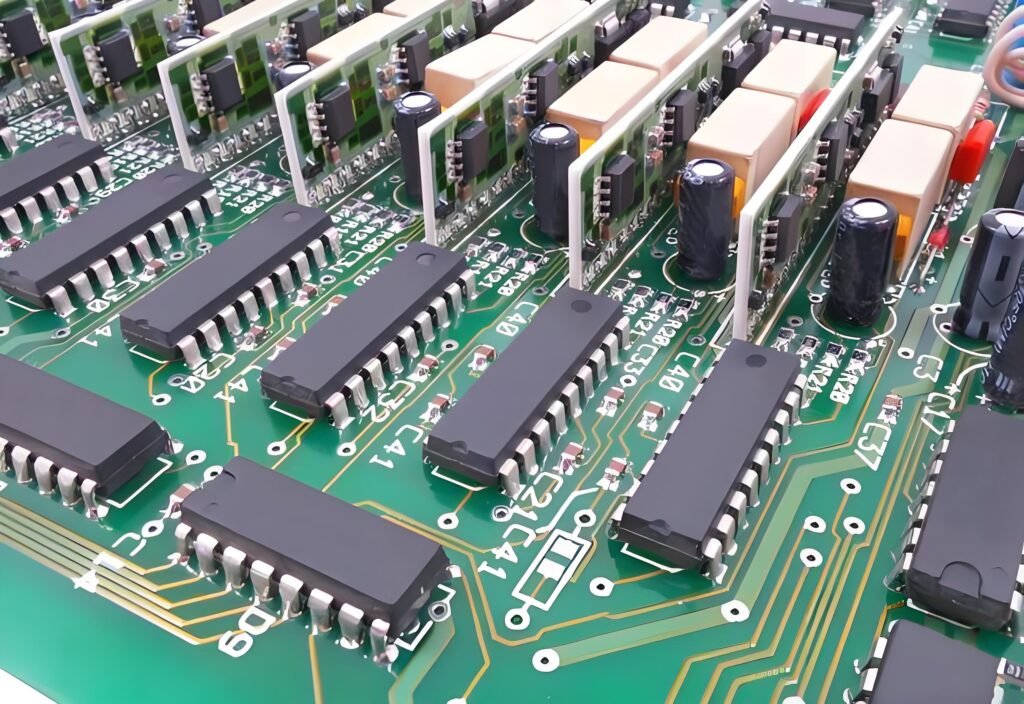
The manufacturing process of blue circuit boards is intricate and precise, encompassing multiple steps to create these complex electronic components. Renowned for their striking appearance, blue circuit boards find applications in a wide range of electronic devices, from smartphones to aerospace technologies. Let’s explore the detailed step-by-step process involved in producing blue circuit boards:
- PCB Design The first step in the circuit board manufacturing process is the design of the PCB. Engineers and designers utilize computer-aided design (CAD) software to create the layout of the circuit board. This phase involves determining the placement of components, routing traces, and defining the overall size and shape of the board. Special attention is given to the positioning of the blue solder mask, which provides the distinctive color of the circuit board.
- Material Selection Once the design is finalized, the next step is selecting materials for the blue circuit board. The substrate material is typically fiberglass-reinforced epoxy resin, known as FR-4, which provides essential structural support. The blue solder mask, made from a specialized epoxy ink containing pigments, determines the board’s vibrant hue.
- PCB Fabrication The manufacturing process begins with the preparation of copper-clad laminate, which is a thin layer of copper bonded to the FR-4 substrate. The design information is then transferred to the laminate through a process called photolithography. This involves applying a photosensitive layer (photoresist) that is exposed to ultraviolet light through a mask containing the circuit pattern. After exposure, the unexposed photoresist is removed, leaving behind the copper traces required for the circuit.
- Etching Following the photolithography process, the exposed copper traces undergo etching. An etching solution, typically acidic, is used to dissolve unwanted copper, retaining only the necessary electrical paths. The blue solder mask is then applied to the board, covering the copper traces while leaving openings for component placement.
- Solder Mask Application The blue solder mask is applied using a screen printing process. A screen is placed over the PCB, with openings that correspond to areas where the solder mask is needed. Blue ink is then pushed through the screen onto the board. The blue solder mask offers various benefits, including protection from environmental factors, improved insulation, and easier component identification during assembly and maintenance.
- Component Placement After the blue solder mask is applied, the next step involves placing electronic components onto the board. Surface mount devices (SMDs) and through-hole components are soldered to the PCB according to design specifications. The blue solder mask provides clear visual cues for component placement, assisting technicians during the assembly process.
- Soldering Once the components are positioned, the circuit board undergoes a soldering process to secure the components in place. Depending on the type of components used, various soldering methods can be employed, including wave soldering and reflow soldering. The blue solder mask plays a crucial role in protecting non-soldering areas and preventing solder bridges between closely spaced traces.
- Quality Control and Testing Before a blue circuit board is deemed ready for use, it undergoes rigorous quality control and testing. Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) machines and functional testing equipment check for any manufacturing defects or connectivity issues. Any problems identified during testing are rectified before the circuit board is approved for shipment.
- Finalization and Packaging After passing quality control checks, the blue circuit boards are finalized with necessary finishing touches. This may include applying a protective coating to safeguard the board from moisture and other environmental factors. Finally, the blue circuit boards are carefully packaged and prepared for distribution to electronic manufacturers and other clients.
In summary, the manufacturing process of blue circuit boards is a detailed and systematic approach that combines advanced technology and careful craftsmanship, resulting in high-quality components essential for modern electronics.
Applications of Blue Circuit Boards
Blue circuit boards are widely utilized across various electronic devices, playing a crucial role in modern technology. From smartphones to automobiles, these boards enhance the functionality and reliability of numerous consumer and industrial products. In this section, we will explore the diverse applications of blue circuit boards and illustrate how they contribute to the performance and durability of different electronic systems.
The Comparison of Blue Circuit Boards with Other Colors
Traditionally, green has been the go-to color for circuit boards, but in recent years, blue has gained popularity. This section will compare blue circuit boards with other color options, such as red and green, analyzing the advantages and disadvantages of each choice. Understanding these differences will help readers appreciate the unique benefits that blue circuit boards offer, including aesthetic appeal and visibility in complex designs.
Design Considerations for Blue Circuit Boards
When designing blue circuit boards, several key factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance and reliability. This section will delve into the specific design considerations unique to blue PCBs, guiding designers on how to leverage the blue solder mask effectively. By focusing on the interplay between functionality and visual appeal, designers can create circuit boards that not only perform well but also look great in their applications.
Troubleshooting Blue Circuit Boards
Like any electronic component, blue circuit boards can encounter issues. This section will address common problems faced by blue PCBs and provide troubleshooting tips and maintenance advice. While some issues can be resolved independently, we will emphasize the importance of seeking professional assistance for more complex problems, ensuring that users understand when it’s best to consult an expert.
Future Trends in Blue Circuit Board Technology
As technology evolves, so do blue circuit boards. This section will explore the latest advancements in materials, manufacturing techniques, and design aspects related to blue circuit boards. Additionally, we will speculate on future trends and their potential impact on the electronics industry, highlighting innovations that may redefine how these components are utilized in emerging technologies.
Environmental Impact of Blue Circuit Boards
With increasing awareness of environmental issues, electronic waste from discarded devices has become a significant concern. This section will focus on the environmental implications of blue circuit boards and discuss recycling and waste management strategies. We will also explore sustainable practices in PCB production aimed at minimizing the ecological footprint of electronic devices, emphasizing the need for responsible manufacturing and disposal.
Myths and Misconceptions About Blue Circuit Boards
Like any technology, blue circuit boards are surrounded by various misconceptions and myths. This section will debunk common misunderstandings, distinguishing fact from fiction. By clarifying these misconceptions, readers will gain a better understanding of the realities of blue PCBs and their role in modern electronics.
The Future of Blue Circuit Boards
In this section, we will explore the future of blue circuit boards. Based on current developments and trends, we will forecast potential growth and expansion opportunities for blue PCBs. From innovative applications to their integration into the Internet of Things (IoT), the future of blue circuit boards is filled with possibilities, indicating a significant evolution in how these components will be utilized.
Conclusion
Blue circuit boards have evolved from simple electronic components to advanced technologies driving the modern world. The blue solder mask not only enhances their aesthetic appeal but also provides functional advantages, making them a preferred choice across various industries. As technology continues to advance, blue circuit boards will play an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of electronic products, paving the way for innovative applications and improved functionalities.

